Popular Import Export Payment Terms: LC, DAP, DAA, Advance (Detailed Guide)
In international trade, choosing the right payment terms is crucial for ensuring smooth transactions and minimizing financial risks for both exporters and importers. Exporters need to secure payments, while importers want to ensure that goods are delivered as expected. To achieve this balance, different payment terms are used to define the obligations and responsibilities of both parties. In this article, we will explore four widely used export payment terms: Letter of Credit (LC), Documents Against Payment (DAP), Documents Against Acceptance (DAA), and Advance Payment. Understanding these payment methods can help businesses make informed decisions and safeguard their interests in global trade.
1. Letter of Credit (LC)
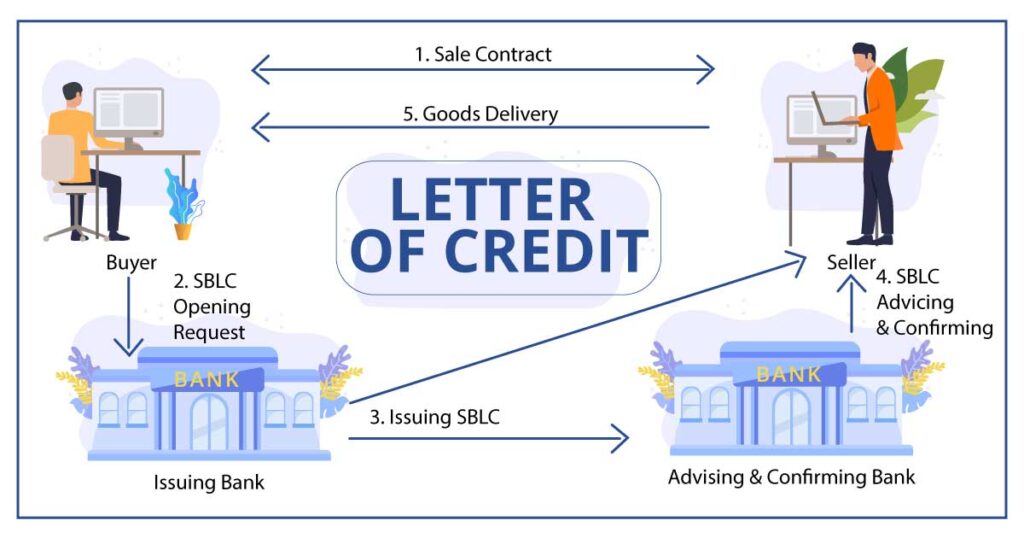
A Letter of Credit (LC) is a financial instrument issued by a bank on behalf of the buyer, guaranteeing payment to the seller once the conditions specified in the LC are met. This method provides a balance of security for both parties, as the seller is assured of payment while the buyer receives goods as agreed. This is one of the most commonly used import export payment terms.
Example:
An Indian exporter ships garments to a buyer in the USA. The buyer’s bank issues an LC, stating that payment will be made once the exporter presents the bill of lading and other required documents. Upon verification, the bank releases the payment to the exporter.
Responsibilities:
- Buyer: Requests the LC from their bank and ensures it matches the contract terms.
- Seller: Ships the goods and submits the necessary documents to their bank.
Advantages:
- For Sellers: Guaranteed payment upon compliance with LC terms.
- For Buyers: Goods are shipped before payment, ensuring order fulfillment.
Cons:
- Involves banking fees and documentation.
- Strict adherence to LC terms is required to avoid discrepancies.
2. Documents Against Payment (DAP)

In Documents Against Payment (DAP), the seller ships the goods and sends the shipping documents to the buyer’s bank. The buyer can only collect these documents, and thus claim the goods, once the payment is made. These import-export payment terms are quite risky for the exporter, as the chances of fraud by the buyer may be quite high.
Example:
A Chinese manufacturer exports electronics to a buyer in Europe. The documents are sent to the buyer’s bank, and the buyer makes the payment to receive them. Only then can the buyer collect the goods from the port.
Responsibilities:
- Buyer: Pays to receive the shipping documents.
- Seller: Ships the goods and forwards the documents to the buyer’s bank.
Advantages:
- For Sellers: Maintains control over goods until payment is received.
- For Buyers: Payment is made only when goods arrive.
Cons:
- Risk of non-payment if the buyer refuses to pay.
- Storage fees may incur if payment is delayed.
3. Documents Against Acceptance (DAA)

Documents Against Acceptance (DAA) allows the buyer to accept a bill of exchange, agreeing to pay at a future date. The buyer receives the shipping documents upon acceptance, enabling them to take possession of the goods before payment.
Example:
An Italian buyer imports machinery from Japan and accepts a bill of exchange due in 60 days. The buyer collects the documents and takes the machinery, paying the seller on the due date.
Responsibilities:
- Buyer: Accepts the bill of exchange, agreeing to pay later.
- Seller: Ships the goods and forwards the documents with a bill of exchange.
Advantages:
- For Buyers: Immediate possession of goods with deferred payment.
- For Sellers: Opportunity to expand the market by offering credit terms.
Cons:
- High risk for sellers due to deferred payment.
- Requires a credit check on the buyer’s financial health.
4. Advance Payment

In Advance Payment, the buyer pays the seller before the goods are shipped. This method is the most secure for sellers but poses the highest risk for buyers.
Example:
A Middle Eastern retailer orders customized products from an Indian manufacturer, paying 50% in advance. Once the manufacturer receives the payment, they begin production and ship the goods upon completion.
Responsibilities:
- Buyer: Makes the payment before shipment.
- Seller: Ships the goods after receiving the payment.
Advantages:
- For Sellers: Eliminates credit risk with upfront payment.
Cons:
- For Buyers: Risk of non-shipment after payment.
- May affect cash flow due to upfront payment.
Mitigation Strategies:
- For Buyers: Verify the seller’s credibility and track record.
- For Both Parties: Consider using escrow services to safeguard payments.
Understanding the pros and cons of each payment term helps businesses select the most suitable method based on their risk tolerance, cash flow requirements, and trust level with trading partners. Proper selection and agreement on payment terms foster successful international trade relationships.
Read Our Other Blogs
We also have other blogs related to Incoterms 2020, Duty Drawback and RODTEP that you can check out for more insights on export benefits, claiming refunds, and enhancing competitiveness in the global market.
FAQs Related to Export Payment Terms

What is a Letter of Credit (LC)?
A financial guarantee by a bank ensuring the seller receives payment upon meeting the conditions specified in the LC.
What is the difference between DAP and DAA?
DAP: Buyer pays to receive the documents.
DAA: Buyer accepts a bill of exchange for future payment.
Is Advance Payment safe for exporters?
Yes, it minimizes credit risk by receiving payment before shipment.
What risks do buyers face in the Advance Payment method in import-export payment terms?
Risk of non-shipment after payment, affecting cash flow.
When should I use Documents Against Payment (DAP)?
When you want to ensure payment before the buyer claims the goods.
Which payment term offers the most security to sellers?
Advance Payment provides maximum security as payment is received upfront.
What are the risks of Documents Against Acceptance (DAA)?
Sellers face a risk of non-payment on the due date.
How does a Letter of Credit work?
The bank guarantees payment to the seller once the LC conditions are fulfilled.
Are banking charges involved in LC transactions?
Yes, banks charge fees for issuing and processing LCs.
Which Import Export Payment Terms is most commonly used?
Letter of Credit (LC) is widely used for international trade due to its security and reliability.
If you want to learn import-export from basics to advanced, including company formation, import-export documents, product research in exports, finding foreign buyers, pre-shipment and post-shipment documentation, GST in exports, payment terms, Incoterms, and more, then watch this 7-hour video by Mr. Keshav Dimri, a successful exporter and brilliant marketer working since 2017.






